INDIAN LANGUAGES
INDIAN LANGUAGES
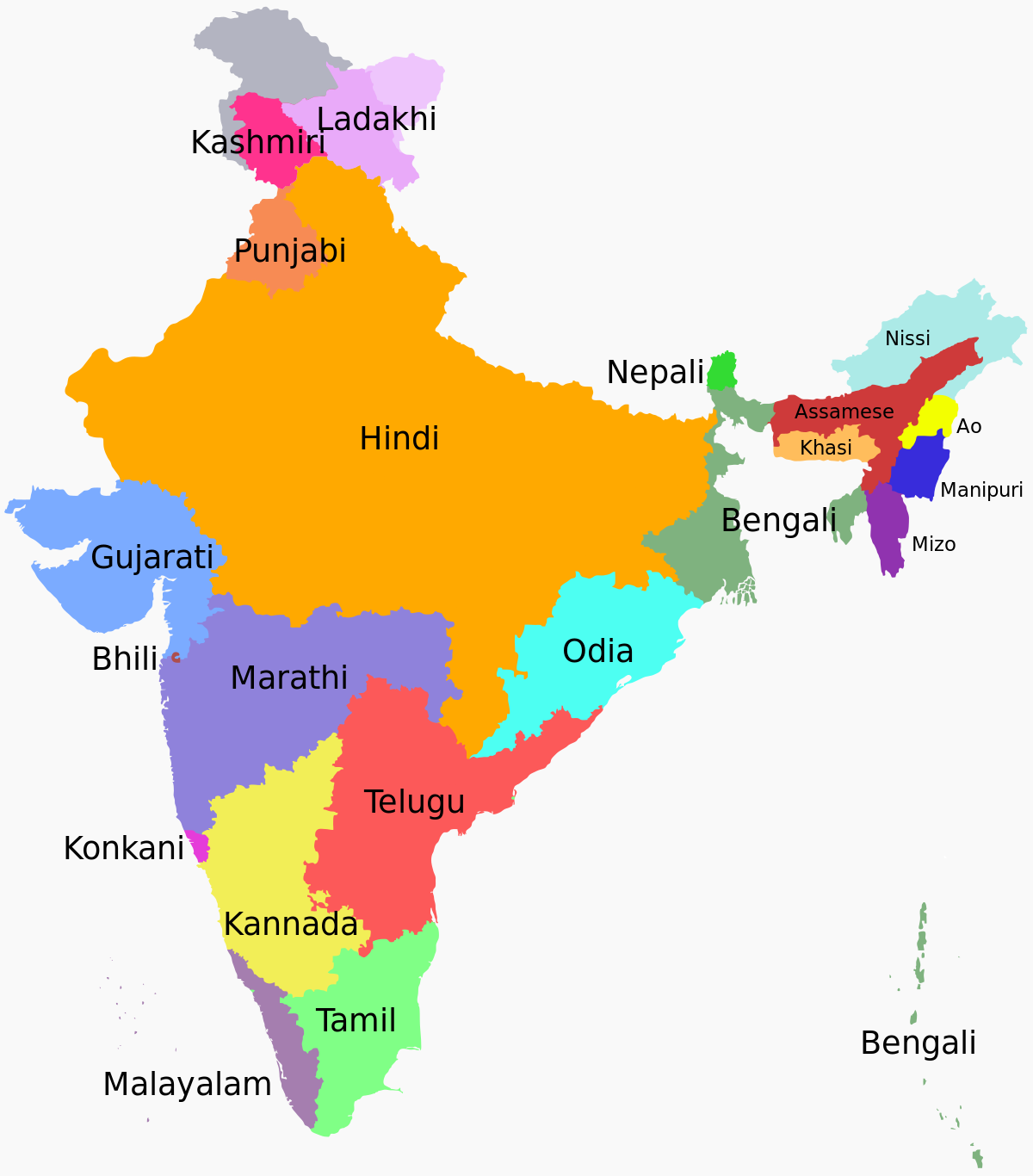
LANGUAGES OF INDIA :- Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 75% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 20% of Indians. Other languages belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan, Tai-Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. India (780) has the world's second highest number of languages, after Papua New Guinea (839).
 Article 343 of the Indian constitution states that
the official language of
the Union government shall become Hindi in Devanagariscript instead of the extant English, but is superseded by English subsequently too as
mentioned in section 3 of the same constitutional article that is put to effect
by The Official Languages Act,
1963. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of
the Union were supposed to become international form of Indian numerals
consequently apart from numerals in English language. Despite the
misconceptions, Hindi is not the national language of India.
Article 343 of the Indian constitution states that
the official language of
the Union government shall become Hindi in Devanagariscript instead of the extant English, but is superseded by English subsequently too as
mentioned in section 3 of the same constitutional article that is put to effect
by The Official Languages Act,
1963. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of
the Union were supposed to become international form of Indian numerals
consequently apart from numerals in English language. Despite the
misconceptions, Hindi is not the national language of India.
LANGUAGES OF INDIA :- Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 75% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 20% of Indians. Other languages belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan, Tai-Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. India (780) has the world's second highest number of languages, after Papua New Guinea (839).
 Article 343 of the Indian constitution states that
the official language of
the Union government shall become Hindi in Devanagariscript instead of the extant English, but is superseded by English subsequently too as
mentioned in section 3 of the same constitutional article that is put to effect
by The Official Languages Act,
1963. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of
the Union were supposed to become international form of Indian numerals
consequently apart from numerals in English language. Despite the
misconceptions, Hindi is not the national language of India.
Article 343 of the Indian constitution states that
the official language of
the Union government shall become Hindi in Devanagariscript instead of the extant English, but is superseded by English subsequently too as
mentioned in section 3 of the same constitutional article that is put to effect
by The Official Languages Act,
1963. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of
the Union were supposed to become international form of Indian numerals
consequently apart from numerals in English language. Despite the
misconceptions, Hindi is not the national language of India.
The Constitution of India does
not give any language the status of national language. English was legislated to be reduced to the status of a
"subsidiary official language" after fifteen years. But this
provision of the constitution was negated by a provision in Section 3, of the
same Article 343 that gave primacy to The Official Languages Act,
1963. The Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists 22
languages, which have been referred to as scheduled languages and
given recognition, status and official encouragement. In addition, the
Government of India has awarded the distinction of classical language to Tamil, Sanskrit, Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam and Odia.
According to Census of India of 2001, India
has 122 major languages and 1599 other languages. However, figures from other
sources vary, primarily due to differences in definition of the terms
"language" and "dialect". The 2001 Census recorded 30
languages which were spoken by more than a million native speakers and 122
which were spoken by more than 10,000 people. Two contact languages have played an important role in
the history of India: Persian and English. Persian was the court language during the Mughal period in India. It reigned as an administrative
language for several centuries until the era of British colonisation English continues to be an important language in India.
It is used in higher education and in some areas of the Indian
government. Hindi, the most widely spoken language in India today,
serves as the lingua franca across much of North
and Central India. However, there have been anti-Hindi agitations in South India, most notably in the state of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. There is also opposition in non-Hindi belt
states towards any perceived imposition of Hindi in these areas.
Comments
Post a Comment